Google Unveils Agent2Agent (A2A): A New Open Protocol for AI Agent Interoperability
The proliferation of AI agents in the enterprise promises significant productivity gains by automating complex and recurring tasks. However, their true potential is often limited by their inability to collaborate across different systems, frameworks, and vendors. To address this challenge, Google has announced Agent2Agent (A2A), a new, open protocol designed to enable seamless interoperability within the growing multi-agent ecosystem.
The Need for Collaboration
As enterprises deploy AI agents for tasks ranging from IT support to supply chain management, the lack of a common communication standard creates silos. A2A aims to break down these barriers, allowing agents built by different developers or on different platforms to interact, share information, and work together on tasks. This interoperability is key to multiplying productivity gains and reducing long-term costs associated with disparate agent systems.
Google notes that A2A complements existing efforts like Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP) and draws on Google's experience in deploying large-scale agentic systems.
A2A Design Principles
The A2A protocol is built upon five core principles:
- Embrace Agentic Capabilities: Focuses on enabling natural, unstructured collaboration between agents, moving beyond rigid tool-based interactions.
- Build on Existing Standards: Leverages familiar technologies like HTTP, Server-Sent Events (SSE), and JSON-RPC for easier integration into existing IT infrastructures.
- Secure by Default: Incorporates enterprise-grade authentication and authorization, aligning with OpenAPI security schemes.
- Support for Long-Running Tasks: Designed to handle tasks that may take hours or days, providing mechanisms for real-time feedback, notifications, and state updates, especially when human intervention is involved.
- Modality Agnostic: Supports various data types beyond text, including audio and video streaming, reflecting the diverse nature of agent interactions.
How A2A Works
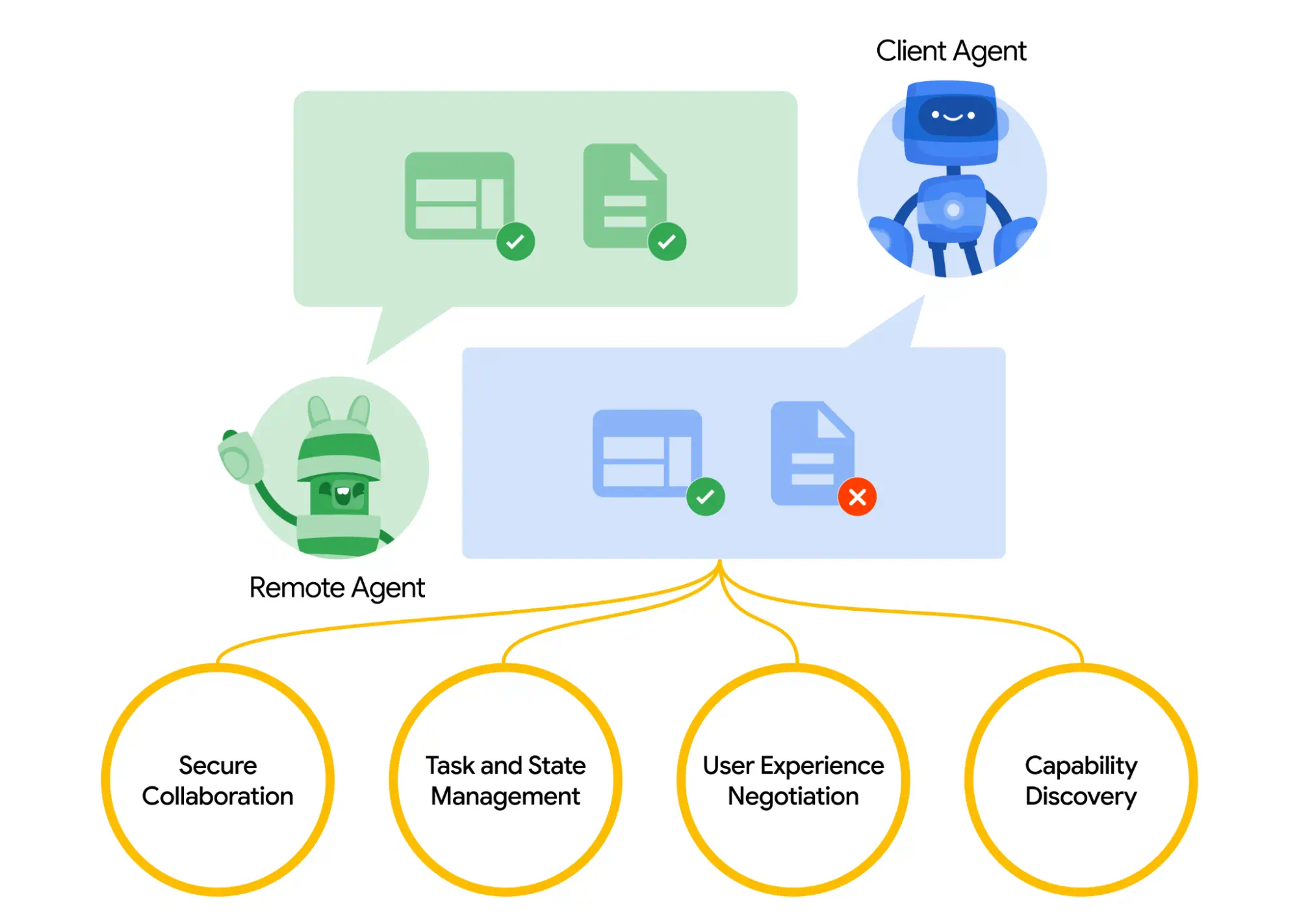
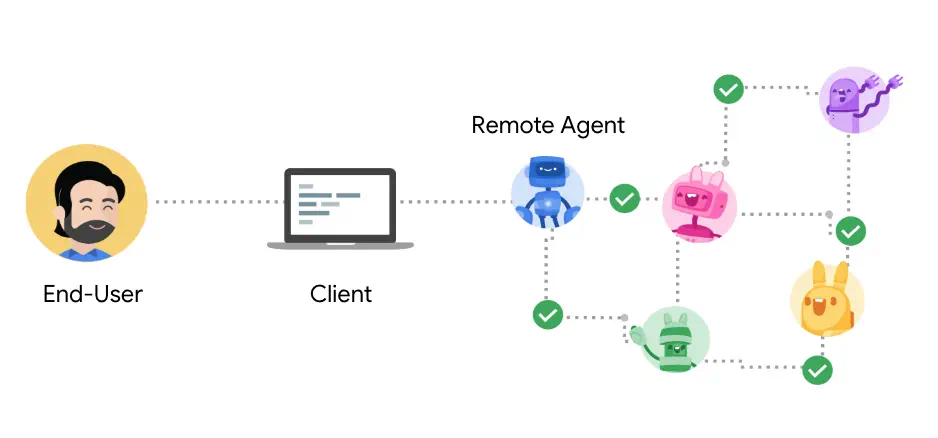
A2A defines a standardized interaction model between a "client" agent (initiating a task) and a "remote" agent (performing the task). Key mechanisms include:
- Capability Discovery: Remote agents advertise their functionalities via a JSON-based "Agent Card," allowing client agents to identify and select the appropriate agent for a given task.
- Task Management: Communication centers around a defined "task" object with a lifecycle. Agents can track progress, exchange status updates (especially for long-running operations), and deliver results as "artifacts."
- Collaboration: Agents exchange messages containing context, replies, artifacts, or specific user instructions to facilitate task completion.
- User Experience Negotiation: Messages contain structured "parts" with defined content types (e.g., images, forms). This allows agents to negotiate compatible formats and UI capabilities (like iframes or video support) for presenting information or interacting with the end-user.
The Future of Agent Interoperability
By providing a standardized, open framework for agent communication, A2A aims to foster innovation and unlock the collective power of diverse AI agents. Google believes this protocol is a critical step towards a future where agents can seamlessly collaborate across boundaries, tackling more complex problems and significantly enhancing workplace automation and productivity.